Parameters
External parameters are passed from the outside when running a report and can be used as conditions in datasets. All external parameters become fields for each report band, so you can use them directly in the template as dataset fields. If any dataset contains a field with the same name, it overrides the external parameter in the corresponding band and the report uses the dataset field value.
External parameters can be passed by the invoking code when running a report through API. Also, the report generator can show a dialog to enter parameters when a user runs the report. In the latter case, you should describe the external parameters in the Parameters tab of the runtime report editor.
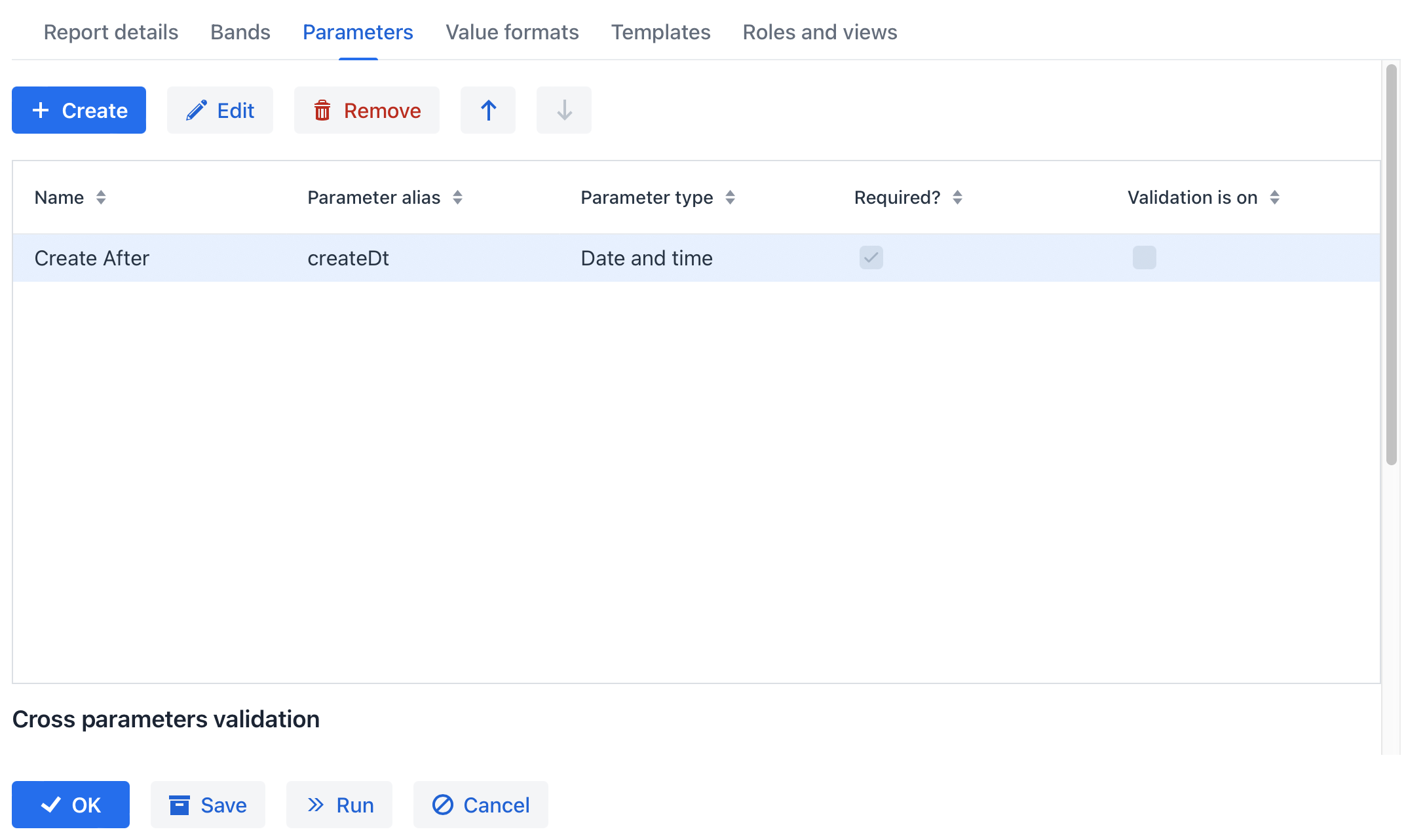
After you click the Create button, the Report parameter dialog is displayed.
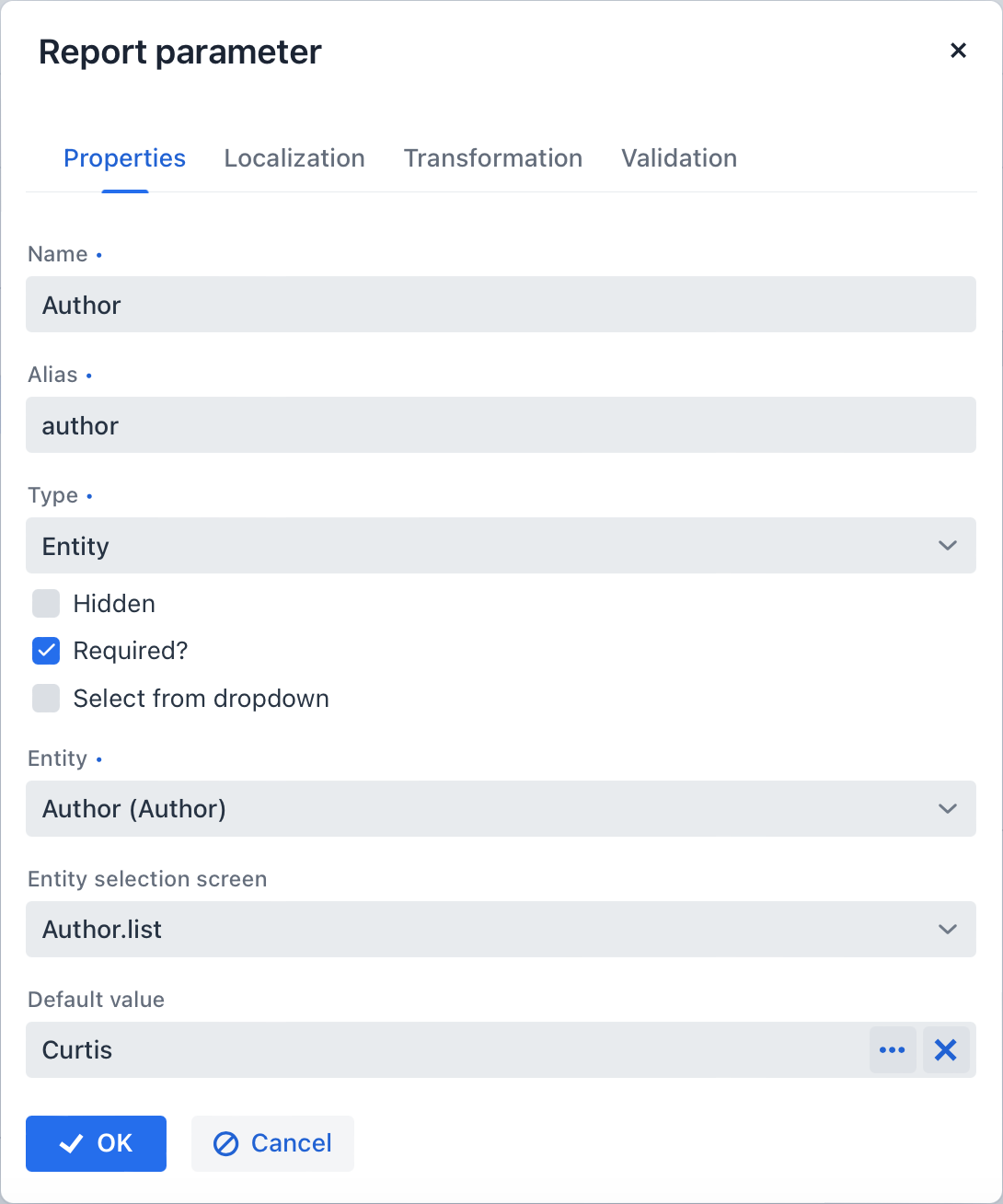
Properties
In the Properties tab, you can define parameter properties:
-
Name - parameter name, as it will appear in the parameter input form when running the report.
-
Alias - parameter alias used to access it in datasets.
-
Type - parameter type.
-
Hidden - flag that defines whether the request for parameter should be hidden from users.
-
Required? - flag determining if the parameter is mandatory.
-
Default value - defines the parameter value that will be used by default if no other value is selected by the user.
The parameter type can be one of the primitive types (String, Number, Boolean) or a temporal type. You can also choose Enumeration, Entity, or List of entities as a parameter type. Based on the selected type, additional fields are required:
If the Entity or List of entities parameter type is selected:
-
Entity - entity to use as parameter.
-
Entity selection view - optional view identifier, which will be used to select entity instances. If the view is not specified, selection will be made from a special generic view for all entities.
If the Enumeration parameter type is selected:
-
Enumeration - enumeration to use as parameter.
If the temporal parameter type is selected (Date, Time or Date and time):
-
Default date(time) is current - a flag that defines whether the current timestamp will be used as the default parameter value.
Localization
In the Localization tab, you can define the parameter name for different locales. In order to do this, you should enter the locale_name = parameter_name pairs, for example:
de = das BuchTransformation
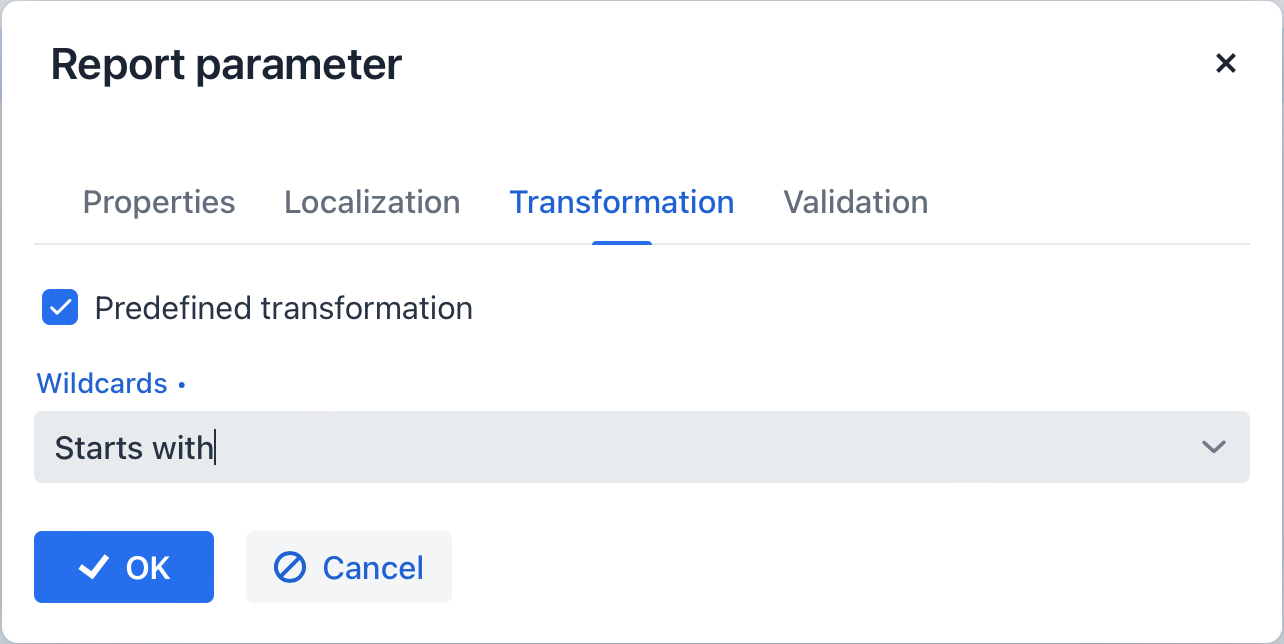
In the Transformation tab, you can apply a Groovy script to the parameter before using it in the report.
A Groovy script should return a new parameter value. The following variables are passed into the script:
-
params- parameters map is available by aliasparams. -
paramValue- the current parameter value is available in the script asparamValue. -
dataManager- an object of theDataManagertype that provides CRUD functionality. -
metadata- an object of theMetadatatype that provides access to the application metadata. -
applicationContext- an object of theorg.springframework.context.ApplicationContexttype that provides access to managed beans.
For example:
return "%" + paramValue + "%"You can also use predefined transformations that add wildcards for text (String) parameters:
-
Starts with, -
Ends with, -
Contains.
In the Validation tab, you can define a Groovy script with some conditions for the parameter validation, see the details below.
Validation
You can validate an input parameter and/or define the cross-parameter validation.
-
You can enable validation of each parameter in the Validation tab by checking the Validate checkbox. The validation logic is specified by a Groovy script. The script should check the parameter value and call the
showErrorMessage()method if the value is not valid. This method will show the user an alert with the given message about the report validation errors.The script receives the following parameters:
-
value- the parameter value entered by the user. -
applicationContext- an object of theorg.springframework.context.ApplicationContexttype, providing access to managed beans. -
currentAuthentication- an object of theio.jmix.core.security.CurrentAuthenticationtype associated with the currently authenticated user. -
dataManager- aDataManagerobject for performing CRUD operations. -
metadata- aMetadataobject providing access to application metadata. -
showErrorMessage- a method that triggers validation failure if called within the script.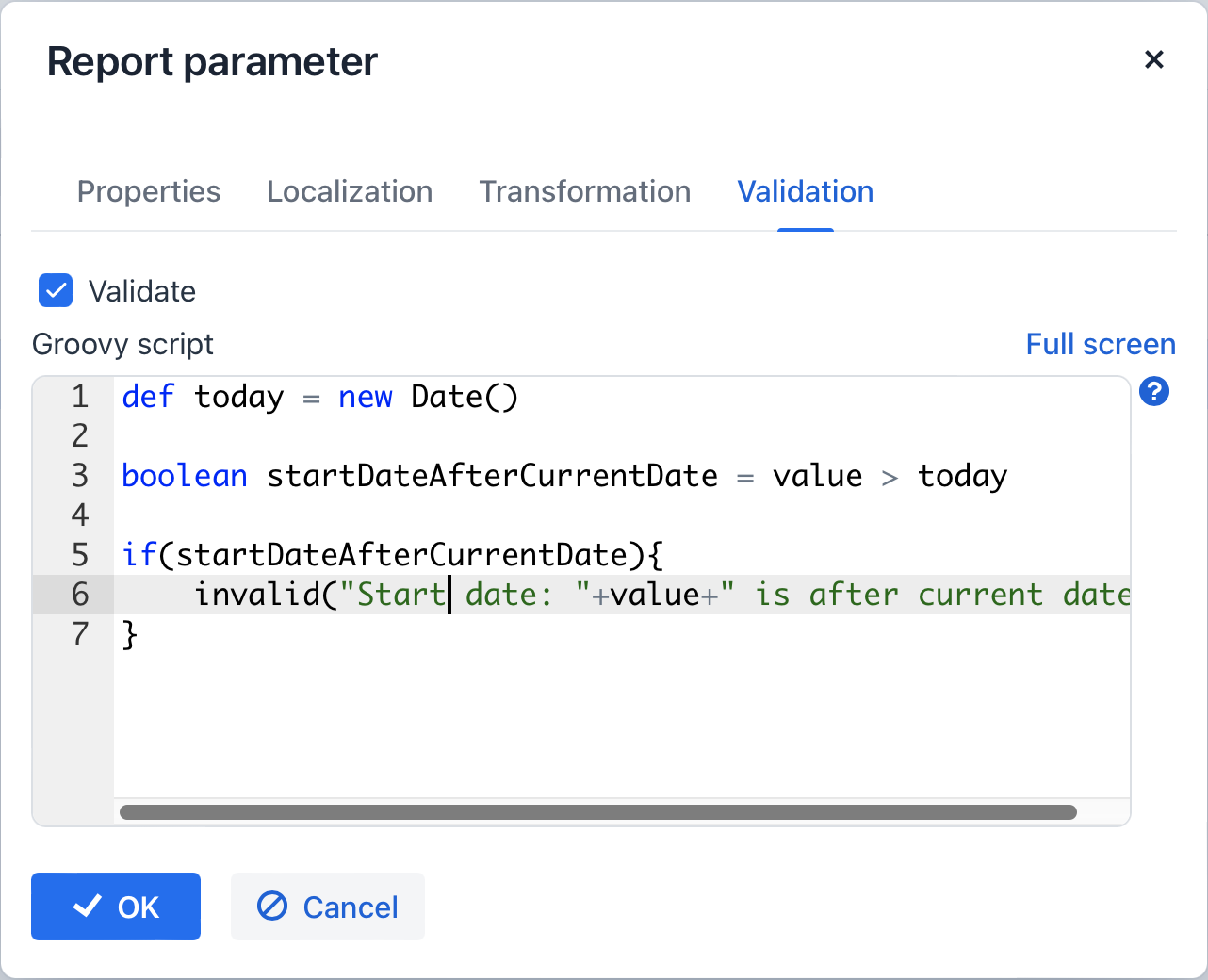
-
-
Cross-parameter validation can be enabled by checking the Validate checkbox in the Cross parameters validation section of the Parameters tab. Validation logic is defined using a Groovy script. This script should verify the consistency of parameter values and call
showErrorMessage()if inconsistencies are found. This method displays an alert to the user, indicating report validation errors.In addition to the parameters listed previously, the script also receives the
paramsvariable, a map containing the external report parameters.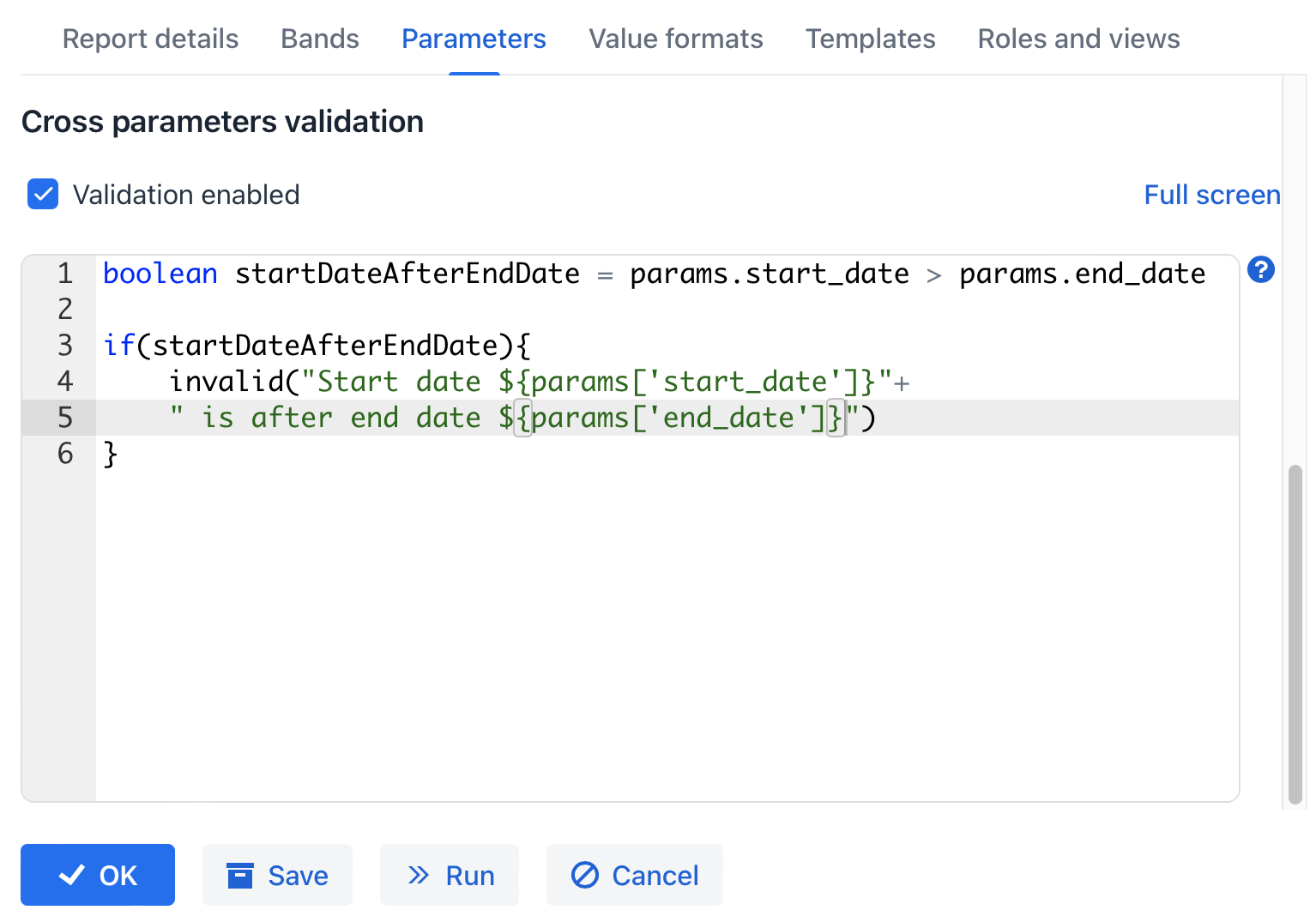
@InputParameterDef Annotation
The @InputParameterDef annotation allows you to define an input parameter when creating a report at design time. Input parameters are passed externally when running a report and can be used as conditions in datasets.
To implement additional logic, create a method annotated with @InputParameterDelegate.
The @InputParameterDef annotation has the following attributes:
-
alias- unique alias used to access the parameter in datasets. -
name- input parameter name. You can use themsg://prefix to refer to a localized message. -
required- specifies whether the parameter is mandatory. Default:false. -
type- data type of the parameter defined by theParameterTypeenum:-
DATE- date, without time. Value class:java.util.Date. -
TEXT- text string. Value class:String -
ENTITY- a single entity instance (persistent or DTO). -
BOOLEAN-Booleanvalue. -
NUMERIC- number with an optional decimal part. Value class:Double. -
ENTITY_LIST- ajava.util.Collectionof entity instances (persistent or DTO). -
ENUMERATION- enumeration value, descendant ofEnum. -
DATETIME- date with time. Value class:java.util.Date. -
TIME- time. Value class:java.util.Date.
-
-
enumerationClass- enumeration class forParameterType.ENUMERATIONparameters. -
defaultValue- string representation of the default value used if no other value is selected. Consider usingio.jmix.reports.yarg.structure.DefaultValueProviderdelegate instead for complex types. -
defaultDateIsCurrent- indicates whether the current timestamp will be used as the default value forParameterType.DATE,ParameterType.TIME,ParameterType.DATETIMEtypes. Default:false. -
entity- additional parameters forParameterType.ENTITYandParameterType.ENTITY_LISTtypes defined by @EntityParameterDef. -
predefinedTransformationEnabled- enables predefined transformation forParameterType.TEXTparameters, useful when the parameter is used in query conditions for SQL and JPQL datasets. Default:false. -
predefinedTransformation- type of predefined transformation forParameterType.TEXTparameters defined by thePredefinedTransformationenum:STARTS_WITH,CONTAINS,ENDS_WITH. Default:CONTAINS. -
hidden- determines whether the request for parameter should be hidden from users. Default:false.
@InputParameterDelegate Annotation
The @InputParameterDelegate annotation defines a delegate method that implements logic related to an input parameter.
Requirements:
-
The method must have no parameters.
-
The method must return one of the supported functional interfaces.
Supported interfaces:
-
DefaultValueProvider- provides a default value for the parameter. -
ParameterValidator- validates the parameter value. -
ParameterTransformer- transforms the parameter value.
The @InputParameterDelegate annotation has the alias attribute, which is an alias of the input parameter declared in the current report definition.
@EntityParameterDef Annotation
Defines additional parameters for input parameters of type ParameterType.ENTITY and ParameterType.ENTITY_LIST.
It has the following attributes:
-
entityClass- entity class of the parameter. Default:void.class. -
component- UI component type used to inputParameterType.ENTITYparameter values when launching a report from the UI. Thecomponentattribute accepts the followingEntityInputComponentenum values:-
OPTION_LIST- EntityComboBox component is used. Options are loaded with a JPQL query. -
LOOKUP_VIEW- EntityPicker component is used, which opens a lookup view. Default value.
-
-
optionsQueryJoin- JOIN clause added to the JPQL query that loads options. -
optionsQueryWhere- WHERE clause added to the JPQL query that loads options. -
lookupViewId- ID of the lookup view opened to selectParameterType.ENTITYorParameterType.ENTITY_LISTparameter values.
