Script Task
Overview
A script task is a task that executes a Groovy script when it is reached in the process flow.
Commonly, script tasks are used when we need to initialize process variables, set default values, evaluate expressions, and do some calculations — everything that can be done with a small piece of code.
But not limited to the above. You can implement any business logic inside your script, it’s up to you.
|
Jmix BPM supports only Groovy scripts. But the original Flowable product allows JavaScript as well. Be attentive when importing process models from external sources. |
A script task is visualized as a typical BPMN 2.0 task (rounded rectangle), with a small 'script' icon in the top-left corner of the rectangle.
A script task is defined by specifying the script and the scriptFormat.
<scriptTask id="script-task" name="Script task"
scriptFormat="groovy" (1)
flowable:resultVariable="result"> (2)
<script>
printlnt "This is a script" (3)
return "OK"
</script>
</scriptTask>| 1 | — Script type (only Groovy) |
| 2 | — Result variable (optional) |
| 3 | — Script body |
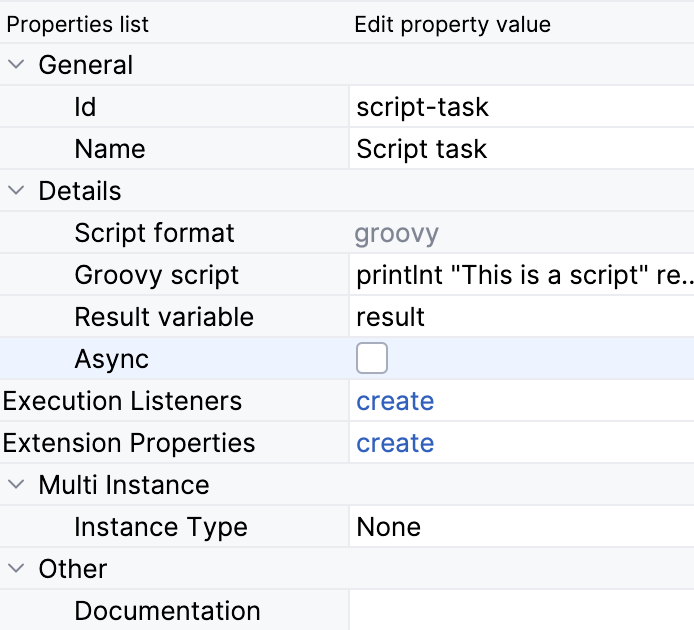
Properties
Script task has the following specific properties:
-
scriptFormat: an extended attribute that specifies the script language; currently, only Groovy is supported. See Groovy language documentation.
-
script: the script to execute. Use the Script editor to edit it.
-
resultVariable: This optional attribute saves the evaluation result in a variable with the specified name within the execution context. See details.
| The script body cannot be empty, otherwise it causes a parsing error during deployment. |
Variables in Scripts
All process variables that are accessible through the execution that arrives in the script task can be used within the script. In this example, the script variable 'inputArray' is in fact a process variable (array of integers).
<script>
sum = 0
for ( i in inputArray ) {
sum += i
}
</script>It’s also possible to set process variables in a script, simply by calling
execution.setVariable("variableName", variableValue)By default, no variables are stored automatically.
Beans in Scripts
Beans may be accessed in scripts by their names. The following Groovy script calls the doSomething method from MyBean and sets the result in the execution context as a variable:
res = MyBean.doSomething()
execution.setVariable("doSomething", res)| The primary and recommended way to call a bean is with a Service Task. If you need to use Groovy logic along with Java bean calls, call the bean from a Service Task before or after the Script Task and let them communicate via process variables. |
Script Result
The return value of a script task can be assigned to an existing process variable or a new one. To specify the target variable, you can set it in the Result variable field in the properties panel of the script task.
When a script task is executed, the script’s return value will be automatically assigned to the specified process variable. If the variable doesn’t exist, Flowable will create a new one with the same name as the Result variable field.
By leveraging the Result variable field, you can integrate the results of script tasks into your process variables, enabling you to store, manipulate, and access data throughout the process execution.
The return value of a script can be assigned to an existing variable or to a new process variable. You can set it in the Result variable field in the properties panel.
In the script, you can use the 'return' operator. For example:
def a = "abc"
return aIf there is no 'return' in your script, as a result will be taken result of the last line, in this example it’d be "JMIX".
String a = "abc".toUpperCase()
String b = "jmix".toUpperCase()