Using DMN 1.3
BPMN and DMN (Decision Model and Notation) notations are designed for collaborative work. When modeling a complex decision, a BPMN diagram can become too complicated. In this case, it’s better to model the decision-making process in DMN and then return control to BPMN.
You can invoke a DMN table from a process by adding a Business Rule Task element. Input values are defined according to the business rules specified in the table. As a result, you will obtain output values in the specified format.
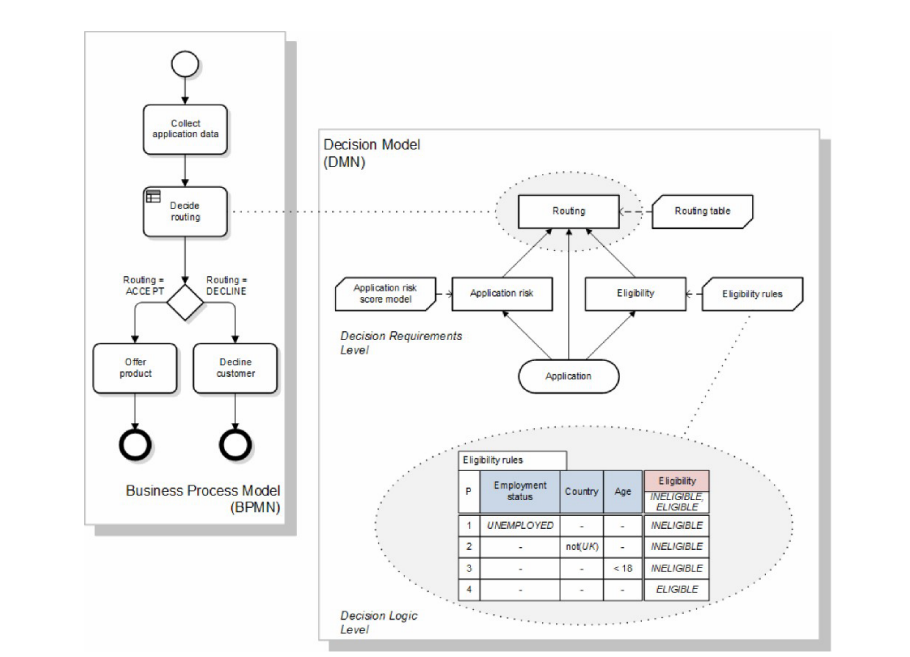
| NOTE: DMN is a graphical notation similar to BPMN, with its own diagrams. However, in practice, software vendors do not implement the full notation and only use DMN tables representing business rules. Jmix BPM only supports DMN tables. |
DMN Engine
Jmix BPM uses the Flowable DMN engine. It supports multiple decision models and provides flexible output processing capabilities. Access to the engine can be obtained programmatically through the DMN API. Additionally, access can be provided for external systems via the DMN REST API.
DMN definition
The root element of the DMN 1.1 schema is the <definitions> element. Within this element, several <decision> elements can be defined.
For readability and ease of maintenance, it is recommended to have only one <decision> element in each file.
|
The <decision> element can have one child element <decisionTable>.
<definitions xmlns="http://www.omg.org/spec/DMN/20151101"
namespace="http://www.flowable.org/dmn"
name="DetermineDiscount">
<decision id="DET_DISC_1" name="DetermineDiscount">
<decisionTable id="determineDiscountTable1" hitPolicy="FIRST">
..
</decisionTable>
</decision>
</definitions>DMN Tools
Jmix BPM add-on provides tools for creating and deploying decision tables that are available in web application:
-
Decision Tables view
-
View Decision Table Modeler view
Modeling Decision Tables
To start creating a decision table, go to the Decision table modeler screen from the main menu of the application.
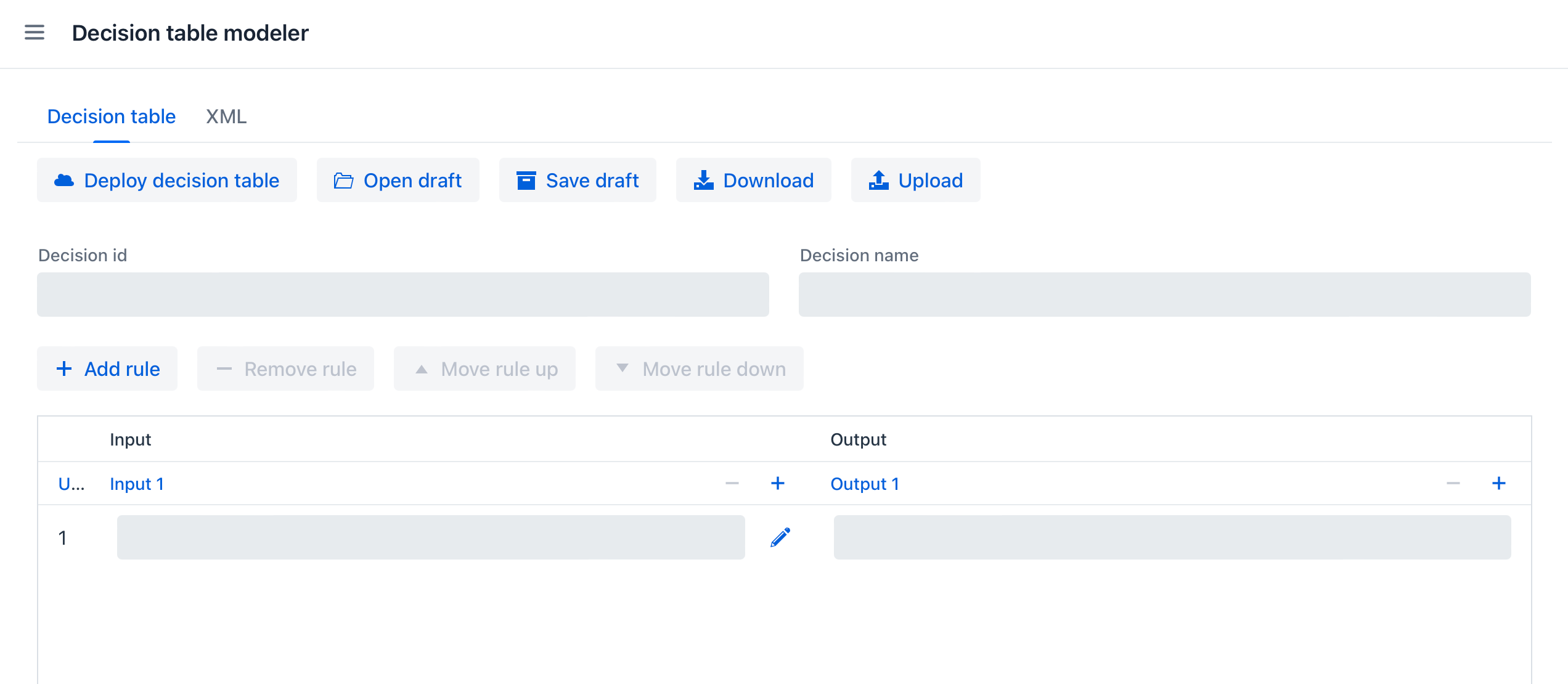
To configure a table, follow these steps:
-
Enter table
idandname -
Define inputs and outputs
-
For outputs, set pre-defined values (if necessary)
-
Create business rules
-
Set hit policy (if there is more than one rule)
After completing the setup, the table can be deployed or saved as a draft.
Defining Inputs and Outputs
Process variables are used as values for inputs and outputs. It is important that the names of these values match the names of the variables. The following types of input and output values are supported:
-
String
-
Number
-
Boolean
-
Date
A new decision table has one input and one output value. You can configure them by setting the name, process variable name, and type. To do this, click on the name:
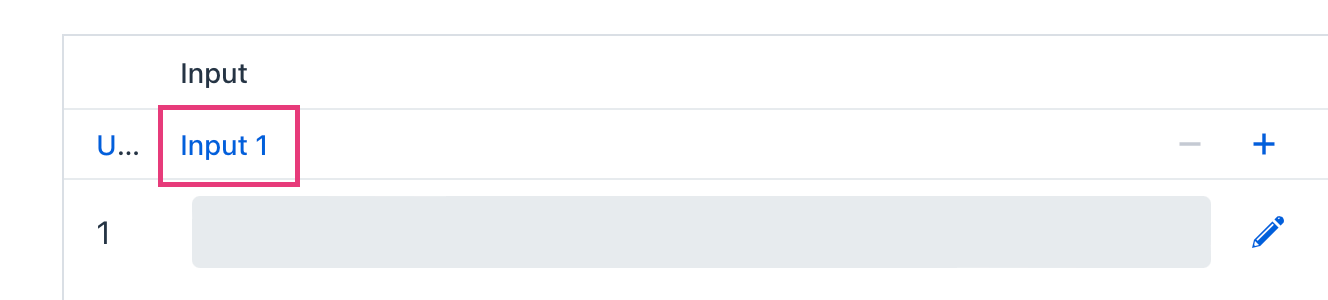
For example, configure the input:
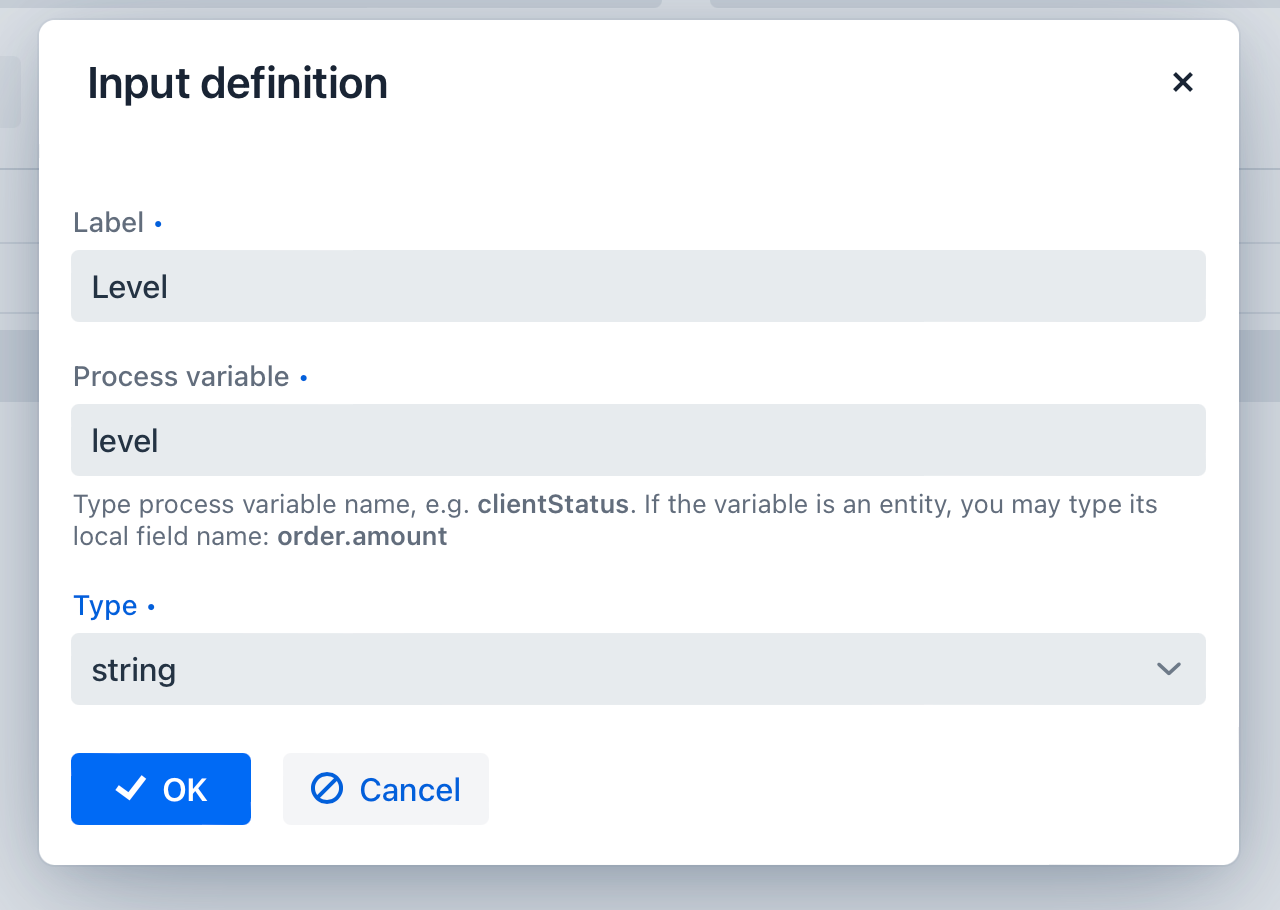
Output values are configured similarly but can have an additional property – Predefined output values. This is used for certain Hit Policies.
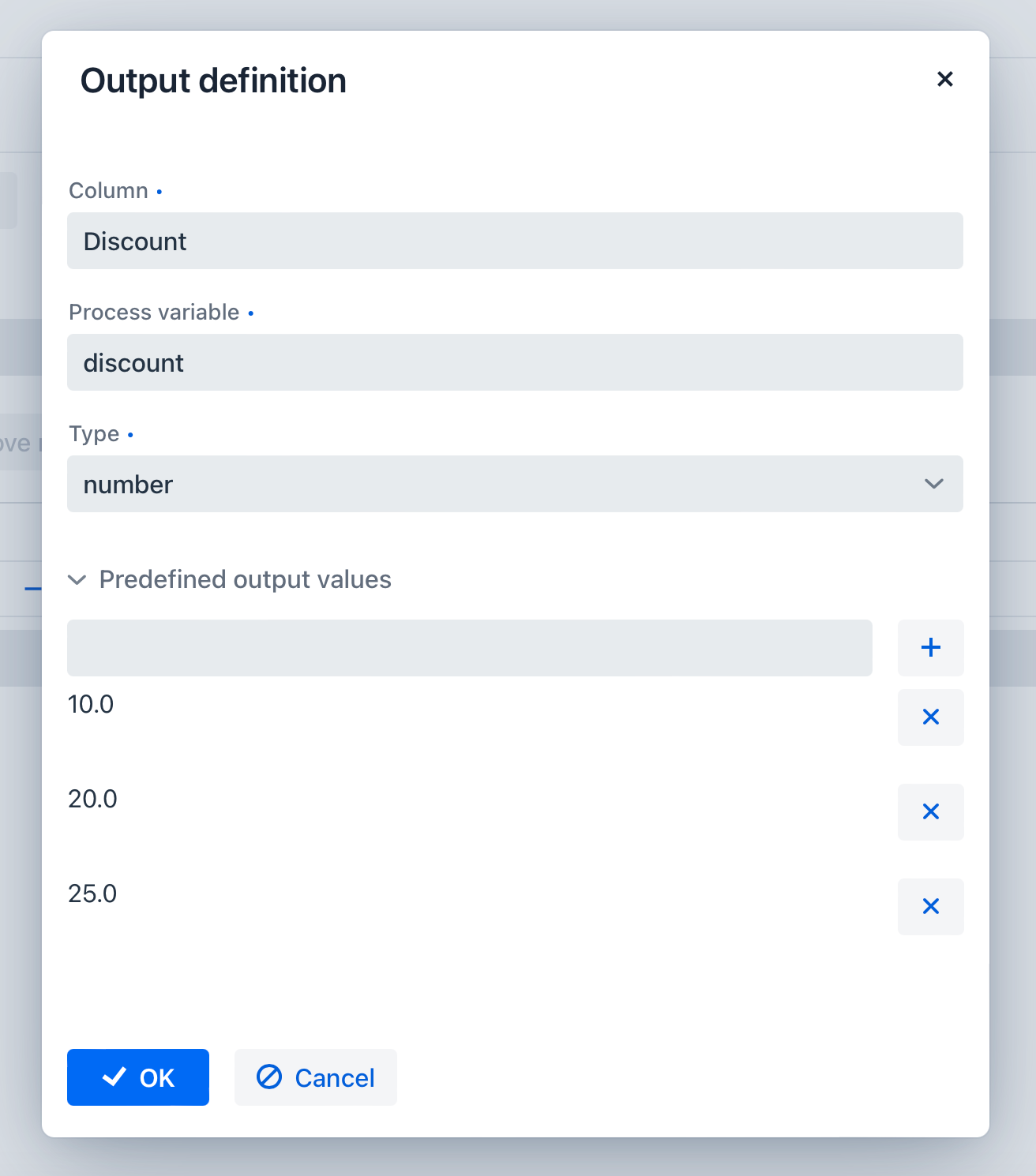
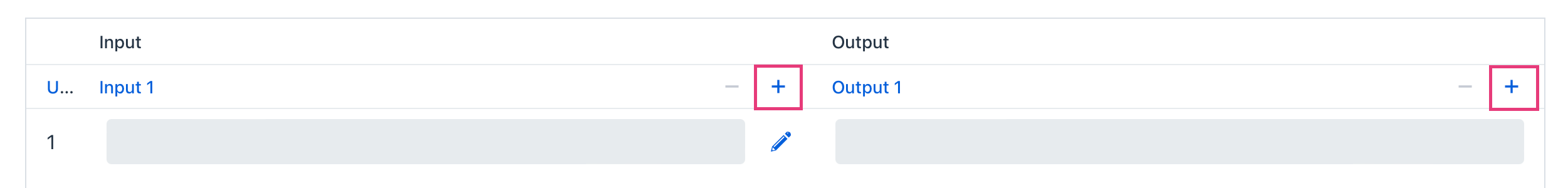
Generally, a decision table contains multiple inputs and outputs. To create an additional one, click the plus sign in the table header:
Hit Policy
Hit policies describe ways to evaluate the rules contained in a decision table. If the rules overlap, meaning that multiple rules match a given set of input values, a result is determined by hit policy. Different hit policies lead to different result and suggest different interpreting of the decision table.
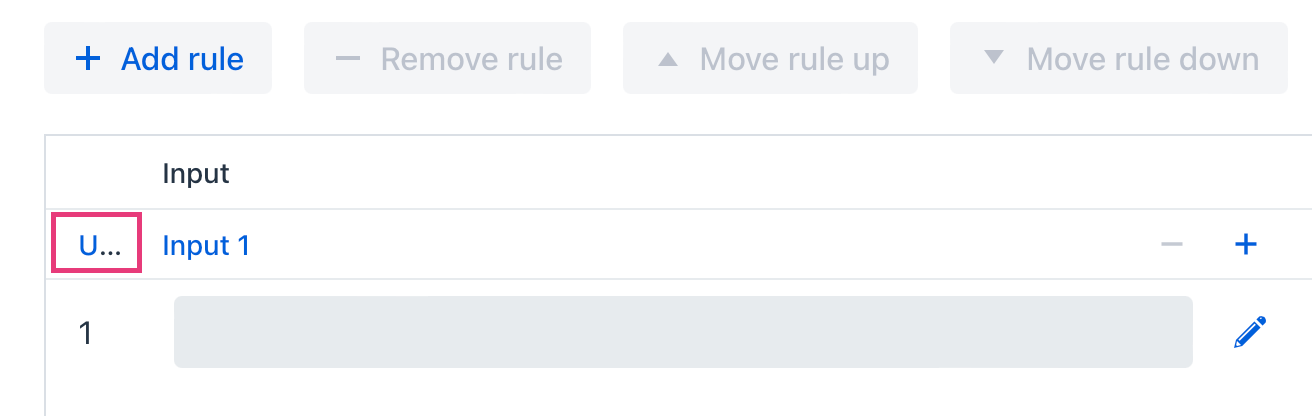
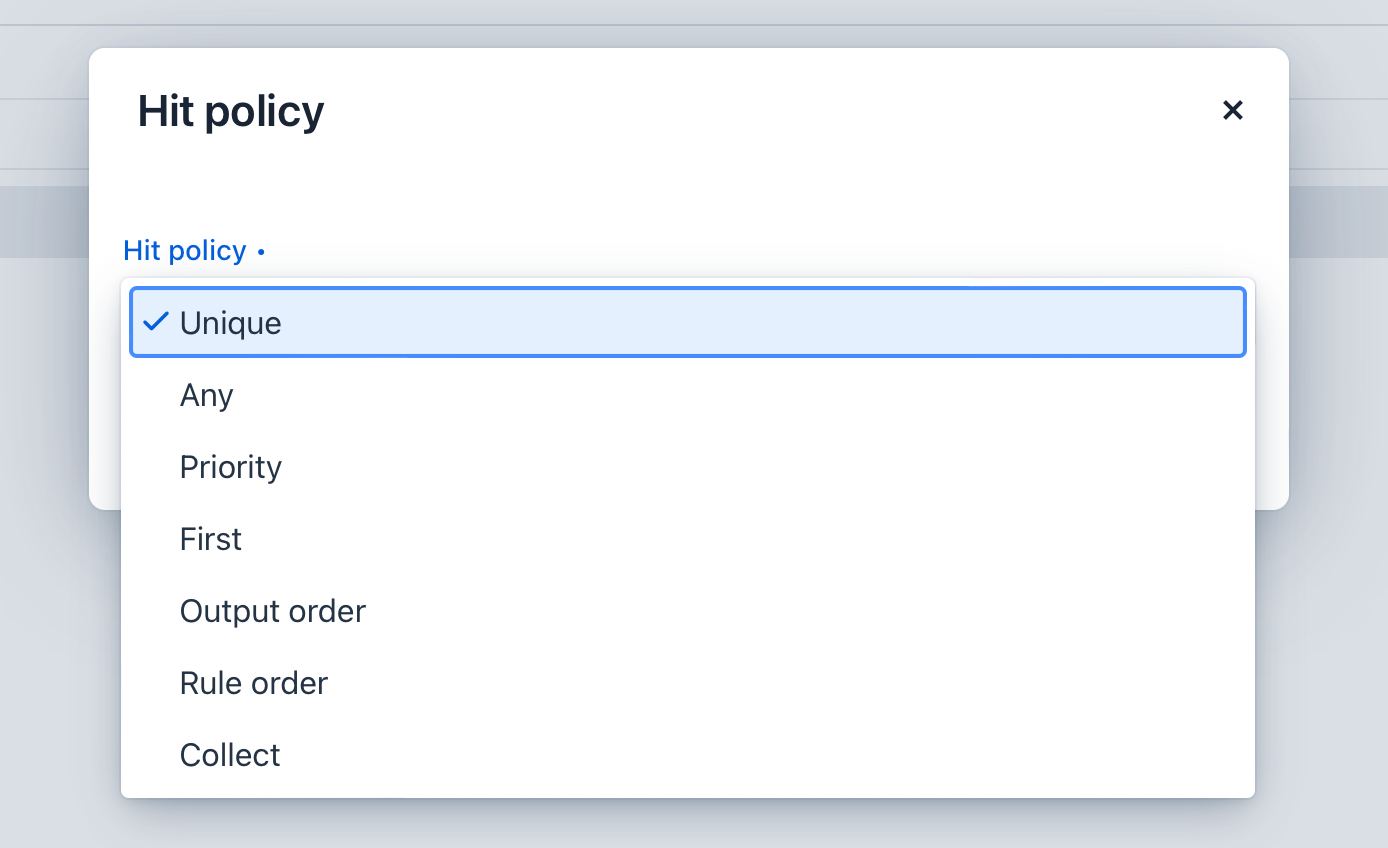
To select a policy, click on the symbol in the top left corner of the table. This symbol corresponds to the initial letter of the selected policy (Unique, Any, Priority, First, Collect, Output Order, Rule Order).
Then select the policy from the dropdown list. The default value is Unique.
Hit policies can be divided into two types: policies that allow a single result and policies that allow multiple results.
Single Result Policies
- FIRST
-
Returns the first result according to the order of rules from top to bottom, and after that, evaluation can be stopped. The last rule often servers as handler.
- UNIQUE
-
Rules cannot overlap; only one rule is applied. Unique is the default selection policy.
- ANY
-
Rules can overlap, but in this case, they must return same result. If there are several matching rules, but they lead to different result, this is considered an error, and the result will be empty and marked as failed.
- PRIORITY
-
Rules can overlap and return different results but only the rule with the highest priority is applied. Priorities are specified in a list, where the most important results come first. It is important that priorities do not depend on the order of the rules.
Multiple Results Policies
For multiple selection policies, the DMN engine returns the result in JSON format. It cannot be implicitly converted to String type variables.
- OUTPUT ORDER
-
All matching rules result in list of output values ordered by priority from high to low. The result will be returned to a process variable named after the decision table.
- RULE ORDER
-
All matching rules result in a list of output values in the order they appear in the decision table.
- COLLECT
-
All matching rules result in a list of output values in arbitrary order. Operators (‘+’, ‘<’, ‘>’, ‘#’) can be applied to the output values; in this case, the table will have a single output result.
-
+(sum): the result of the table will be the sum of all unique output values. -
<(min): the result of the table will be the smallest of all output values. -
>(max): the result of the table will be the largest of all output values. -
#(count): the result of the table will be the count of output values.
-
Example
Below is an example of decision table created in Jmix BPM:
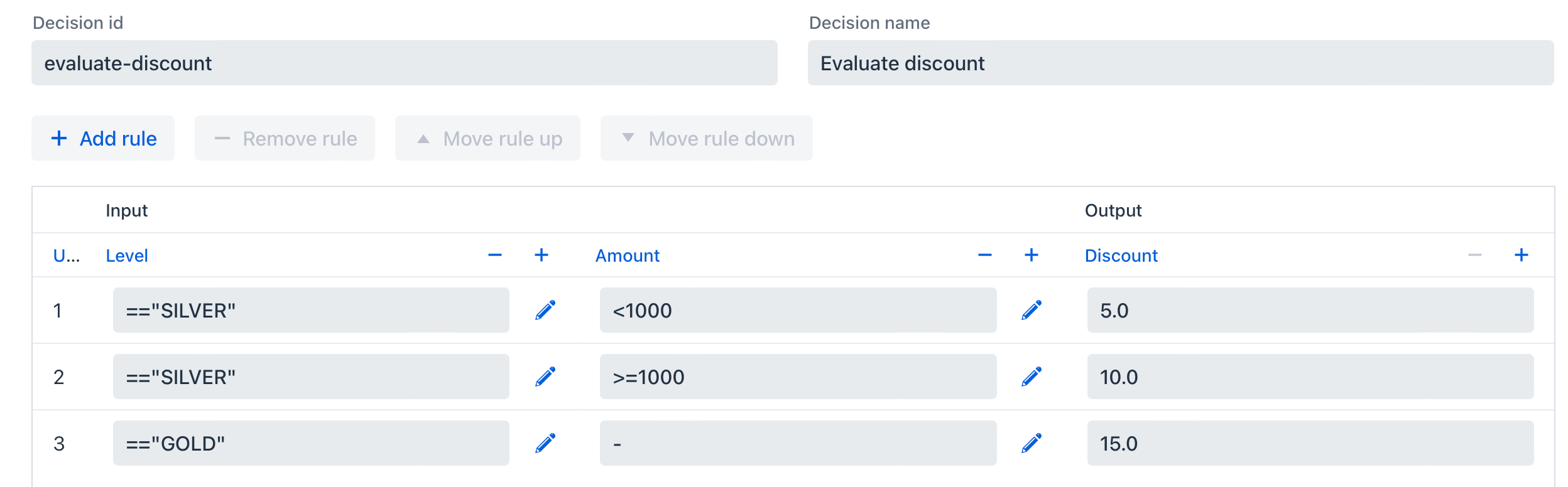
XML representation:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<definitions xmlns="http://www.omg.org/spec/DMN/20151101" namespace="http://www.flowable.org/dmn" name="Evaluate discount">
<decision id="evaluate-discount" name="Evaluate discount">
<decisionTable hitPolicy="UNIQUE">
<input label="Level">
<inputExpression id="input_U9lbk" typeRef="string">
<text><![CDATA[level]]></text>
</inputExpression>
</input>
<input label="Amount">
<inputExpression id="input_dNTA2" typeRef="number">
<text><![CDATA[amount]]></text>
</inputExpression>
</input>
<output id="output_BV1J5" label="Discount" name="discount" typeRef="number">
<outputValues>
<text>"10.0","20.0","25.0"</text>
</outputValues>
</output>
<rule>
<inputEntry id="inputEntry_fBLZR">
<text><![CDATA[=="SILVER"]]></text>
</inputEntry>
<inputEntry id="inputEntry_JtjHs">
<text><![CDATA[<1000]]></text>
</inputEntry>
<outputEntry id="outputEntry_k78f9">
<text><![CDATA[5.0]]></text>
</outputEntry>
</rule>
<rule>
<inputEntry id="inputEntry_ZAVMx">
<text><![CDATA[=="SILVER"]]></text>
</inputEntry>
<inputEntry id="inputEntry_VXpLk">
<text><![CDATA[>=1000]]></text>
</inputEntry>
<outputEntry id="outputEntry_1LiOw">
<text><![CDATA[10.0]]></text>
</outputEntry>
</rule>
<rule>
<inputEntry id="inputEntry_Emrus">
<text><![CDATA[=="GOLD"]]></text>
</inputEntry>
<inputEntry id="inputEntry_qc4Kw">
<text><![CDATA[-]]></text>
</inputEntry>
<outputEntry id="outputEntry_kvA1d">
<text><![CDATA[15.0]]></text>
</outputEntry>
</rule>
</decisionTable>
</decision>
</definitions>
