Introduction
The BPM add-on integrates the open-source Flowable BPM engine into Jmix Platform, bringing to it new tools to design, manage, and automate various complex interactions between people and systems.
Architecture Overview
BPM add-on includes components available in Studio and in the web application at runtime. In Studio, the developer has a Modeler for creating BPMN process models, a Process Form Wizard (in View Creation Wizard), and a BPM section in the Jmix Tool Window.
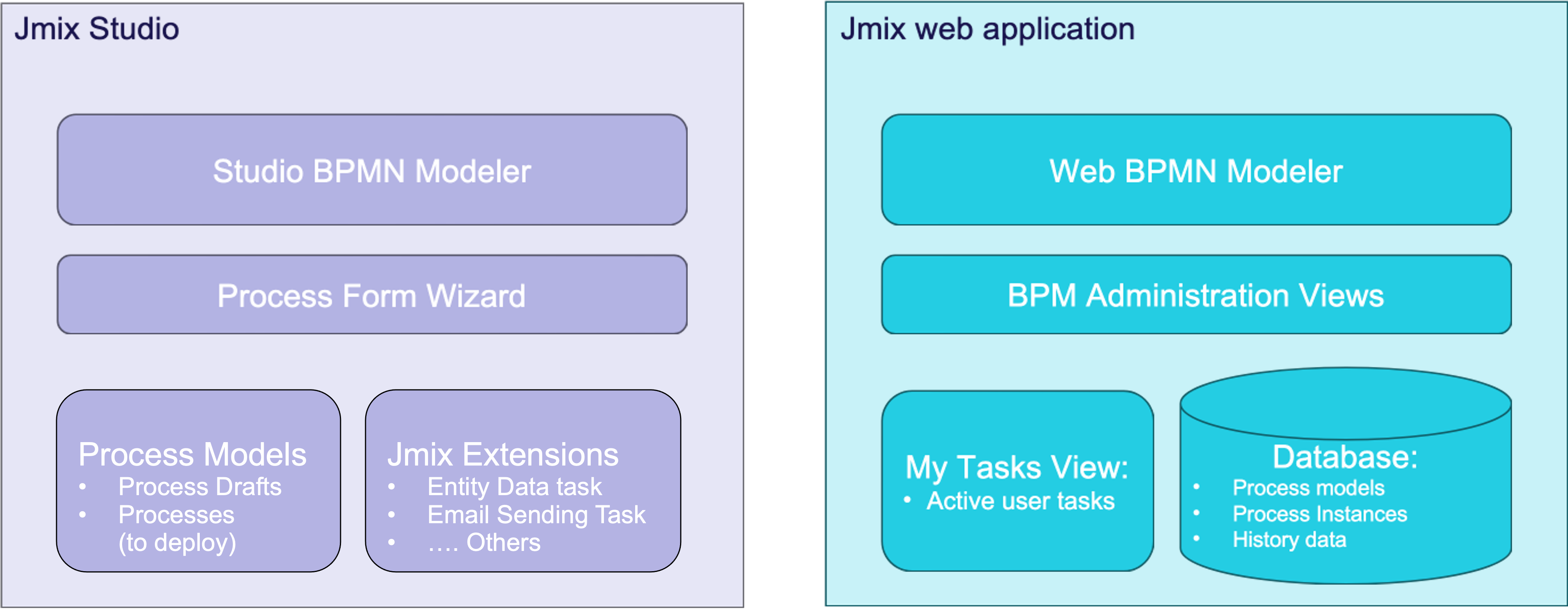
In the web application, you have access to the process Modeler, which offers functionality similar to that of Studio. It includes a set of administrative views as well as user views that enable regular users to start processes and manage their tasks.
Extensions in Process Modeling
When modeling a process, several extensions become available to enhance functionality:
-
Entity Data Task - Allows users to create, modify, and load Jmix Entities directly from the data model.
-
Email Sending Task - Enables users to send emails from within the process.
-
User Providers - Interfaces that allow users to define task performers and candidates programmatically.
-
Jmix BPM Spring Events - Simplifies the implementation of listeners for process events.
-
… and a number of other improvements.
Additionally, the BPM add-on automatically creates the required tables in the database to support these features.
BPMN 2.0
Jmix BPM uses BPMN 2.0 that is a widely accepted and supported standard for modeling and executing automated business processes.
The Business Process Modeling Notation is a graphical notation that depicts the steps in a business process. BPMN depicts the end-to-end flow of a business process. The notation has been specifically designed to coordinate the sequence of processes and the messages that flow between different process participants in a related set of activities.
You can find the official version of BPMN specification at the OMG website: https://www.omg.org/bpmn/
Flowable BPM Engine
Flowable is an open-source Business Process Management (BPM) engine that provides a lightweight, efficient, and highly customizable solution for automating business processes. It is written in Java and supports the BPMN 2.0, CMMN, and DMN standards for modeling and executing processes.
|
Jmix BPM doesn’t support case management using CMMN. |
Flowable is a fork of Activiti (registered trademark of Alfresco). In all the following sections, you’ll notice that the package names, configuration files, and so on, use flowable.
Database Configuration
During the installation process, Jmix creates required database tables in the Main Data Store.
Database Table Names
The database names of Flowable all start with ACT_ (that refers to Activiti product name).
The second part is a two-character identification of the use case.
This use case will also roughly match the service API.
ACT_RE_: RE stands for repository. Tables with this prefix contain 'static' information such as process definitions and process resources (images, rules, etc.)
ACT_RU_: RU stands for runtime. These are the runtime tables that contain the runtime data of process instances, user tasks, variables, jobs, and so on. Flowable only stores the runtime data during process instance execution and removes the records when a process instance ends. This keeps the runtime tables small and fast.
ACT_HI_: HI stands for history. These are the tables that contain historic data, such as past process instances, variables, tasks, and so on.
ACT_GE_: GE means general data, which is used for various use cases.
BPM Roles
During the installation process, the system creates two distinct roles:
-
BPM: administrator - for administrative tasks.
-
BPM: process actor - for participation in processes.
To grant users access to all BPM administrative views, assign them the BPM: administrator role. If users only need to participate in processes, assign them the BPM: process actor role.
Additionally
Alongside the BPM features, incorporating other add-ons can further enhance your application’s capabilities:
-
Quartz – enables scheduled tasks execution, configurable at runtime.
-
Business calendar – enables accounting for working hours, which is especially useful in business processes.
-
Notifications – enables sending notifications to process participants and supervisory personnel. See Sending Notifications section for details.
-
Email Sending — enables sending email messages, it is required when using Email Sending task.
-
Reports – enables building reports based on operational data and process execution statistics.
