Coding Assistance
Jmix Studio provides code completion, code inspections, error highlighting, and quick-fixes, as well as convenient code refactoring and rich navigation capabilities.
Let’s look at what the main coding assistance tools look like.
Code Inspection
Jmix Studio automatically detects and suggests fixing typical programming errors in your project before you compile it.
Depending on the severity level, Studio highlights the code containing some problems in different ways.
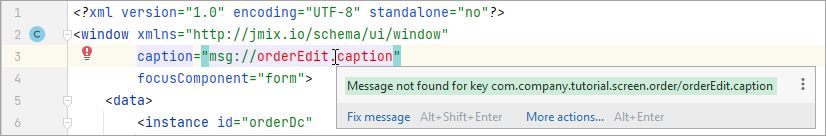
For some inspections, Jmix Studio suggests using quick-fixes.
Quick-Fixes
When some inspection has detected a problem in your code, you can quickly apply a fix in the editor. Place the caret at the highlighted piece of code and press Alt+Enter.

Another way is to place the caret at the highlighted piece of code and click the /
icon. After that, you can view intention actions available in the current context.
Line Markers
A line marker is an icon in the gutter of an editor window. For example, line markers can provide navigation targets to related code:
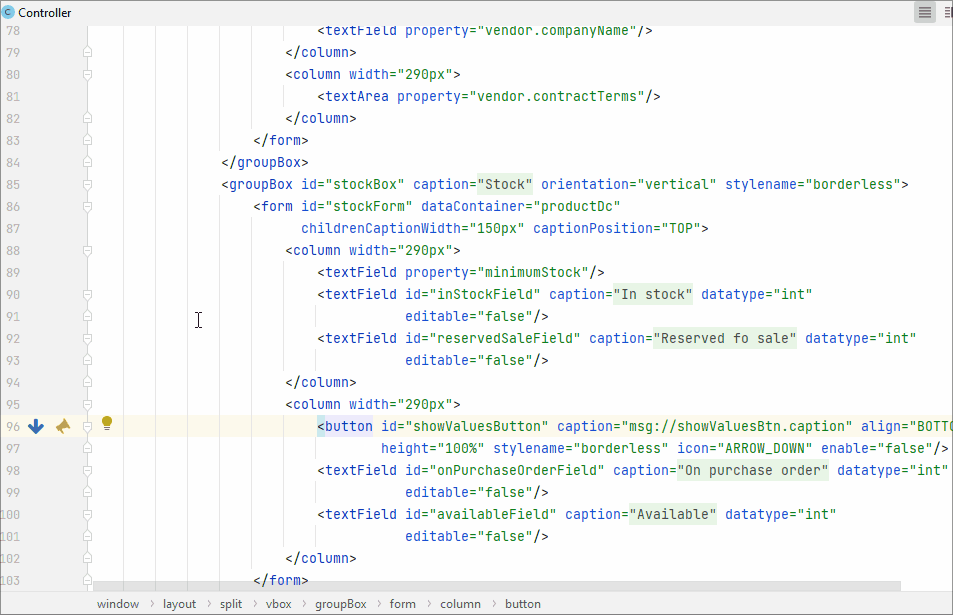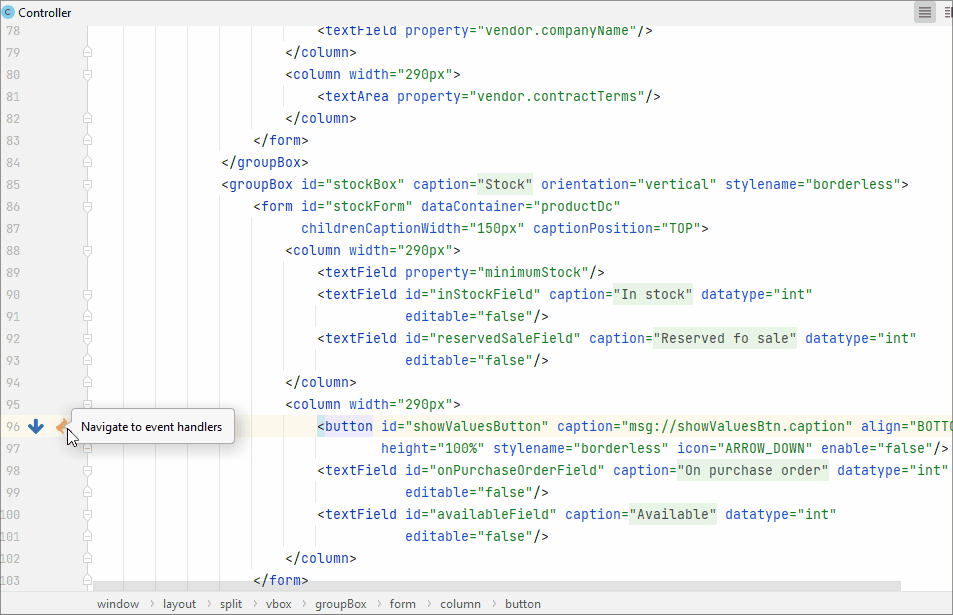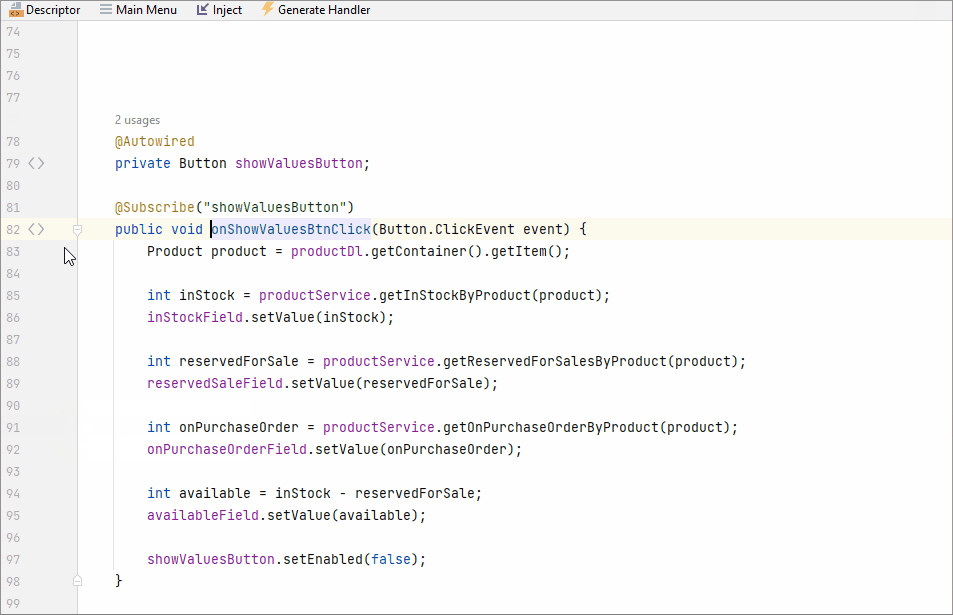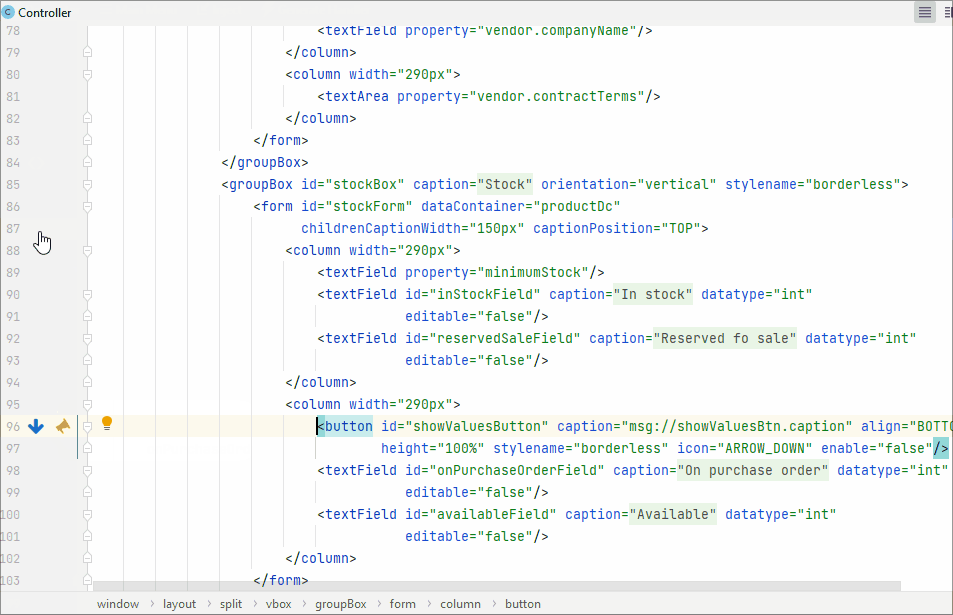
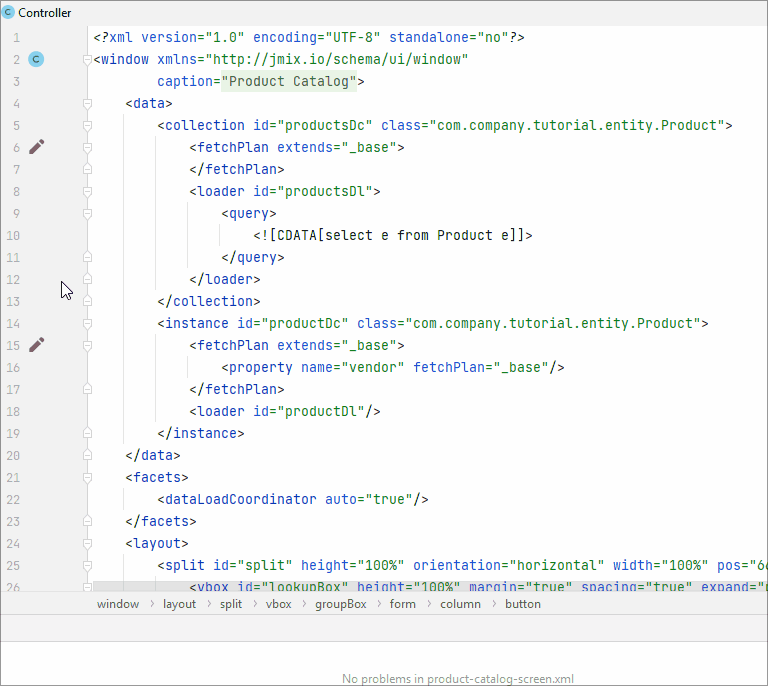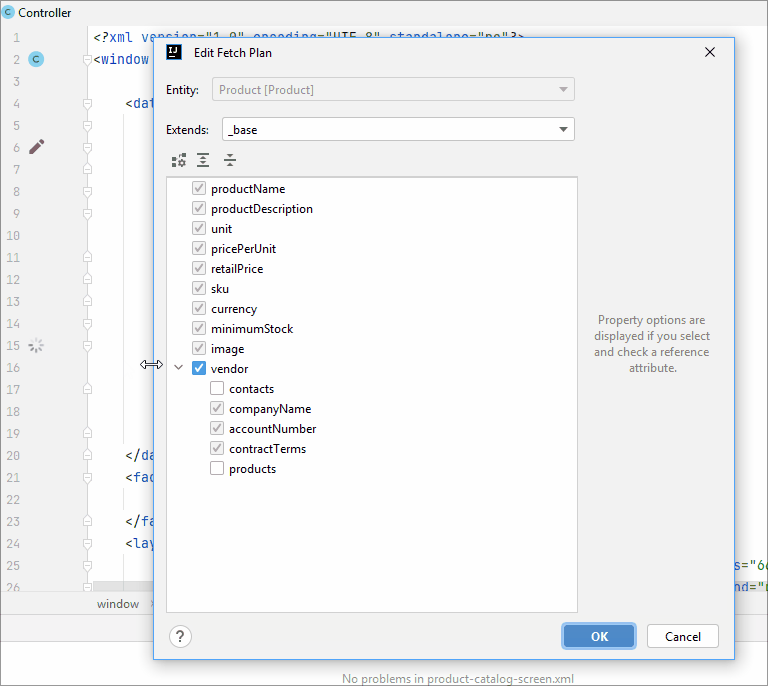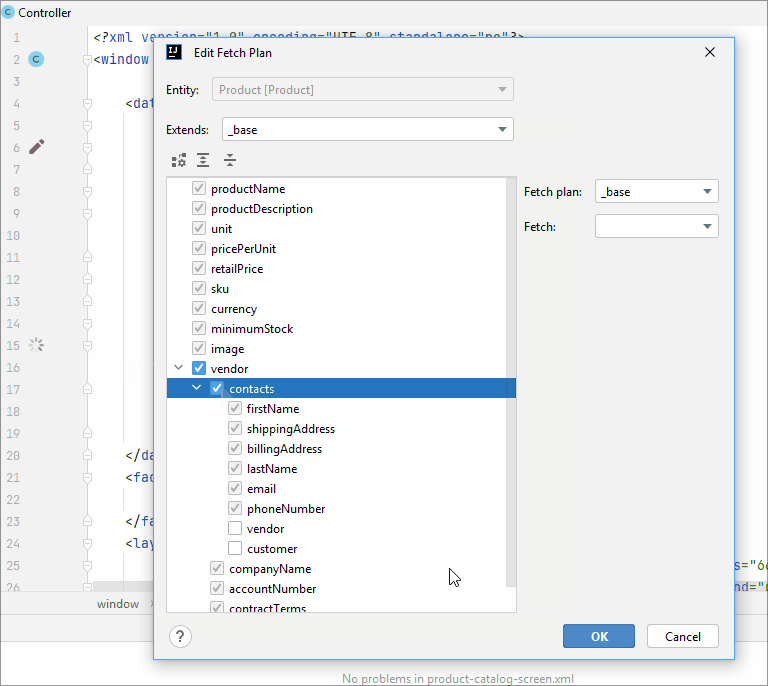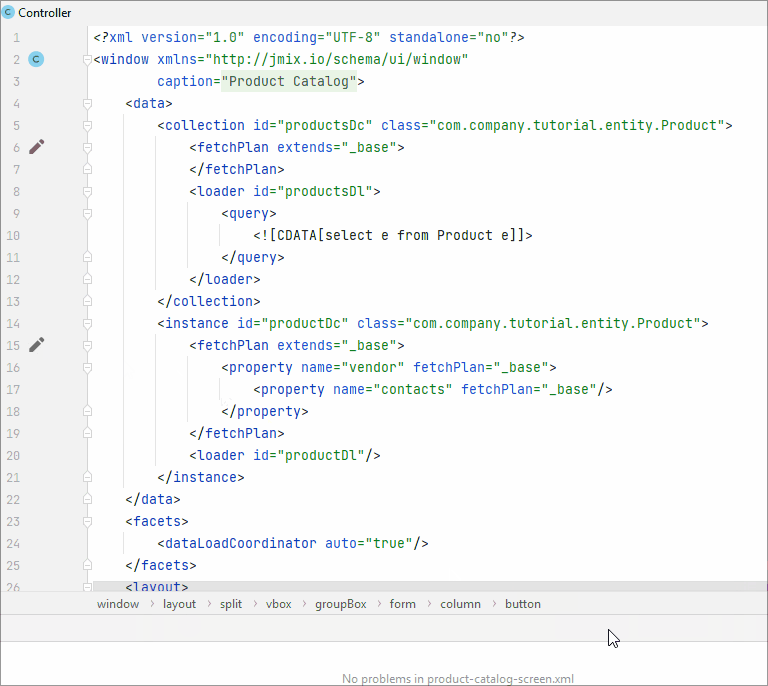
Using line marker, you can edit the fetch plan in the XML descriptor:
Navigation
For example, you can navigate to the injected component or the localized message in the message bundle. Hold Ctrl and left-click the component id or a message key.
Refactorings
You can make changes easily and safely. In the example below, we will change the name of the button.

Using refactorings, you can rename or remove enumerations and entity classes, components, and views.
Scope of Coding Assistance Tool
Let’s look at the main project’s sections, for which various situations of using a coding assistance tool occur.
-
Enumerations and Entities
- Inspections
-
-
The entity with the same table name is unique in the data store.
-
Check for the presence of the @InstanceName annotation.
-
Detect incorrect using of
LAZYfetch type for datatype fields , and@OneToOne,@OneToMany,@ManyToManyand@ManyToOnewith theEAGERfetch type. -
Check for the presence of the JPA annotations for every entity field.
-
Check that the entity and enumeration classes and attributes have localized messages.
-
Check that persistent enumeration attributes are declared according to Jmix conventions - by using identifier type.
-
Check for the duplicates of the
@Versionannotation. -
Check for embeddable attributes that are not marked with the
@Embeddedannotation. -
Check for the presence of a primary key attribute of the entity.
-
- Quick-Fixes and Intentions
-
-
Generate the instance name.
-
Add entity attribute using the designer.
-
Add entity attribute to grids and other components.
-
Edit entity attribute permissions for different resource roles.
-
Edit entity permissions for different resource roles.
-
-
XML Descriptors
- Inspections
-
-
Check property names and paths in
dataGrid, and other components. -
Check the
dataContaineranditemsContainerattributes. They should reference the existing data container in the current view or one of the views which includes the current one as a frame. -
Check the following aspects of Jmix view descriptors:
-
expandattribute; -
iduniqueness.
-
-
Report cases when an entity attribute is used by UI component in XML descriptor but this attribute is not included in the fetch plan.
-
Show error if there is more than one root component in the XML layout.
-
Search for conflicting
width,height, andexpandattribute values in the XML descriptor. -
Check the
hierarchyPropertyattribute. This attribute should be of the same type as an entity in the data container.
-
-
Fetch Plans
-
Check that the
classattribute forfetchPlanis set. -
Search for properties that are declared twice inside the same
fetchPlantag. -
Check if the fetch plan with the current name exists in other fetch plan config.
-
Check if the
fetchPlanproperty contains inner properties or thefetchPlanattribute, then the property should point to an entity. -
Search for properties that are not necessary and can be omitted because they are already included in the fetch plan.
-
-
Controllers
- Inspections
-
-
Check that there is only one installed method referenced to each setter.
-
Inspect components, actions, and data components that are injected into the view controller. Reports if injected fields have an incorrect type.
-
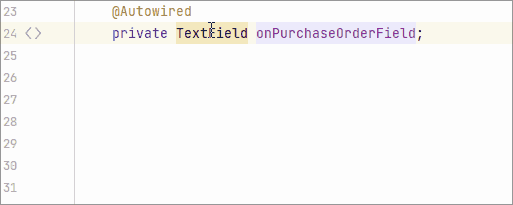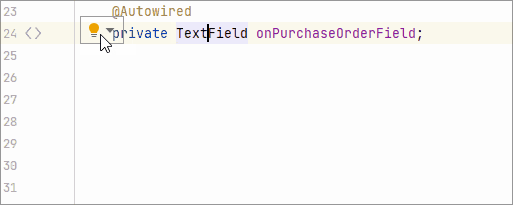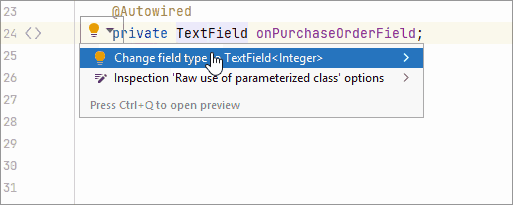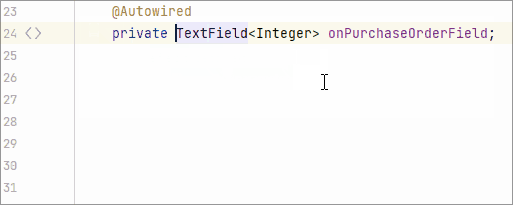
Inspect components injected into the view controller. Reports if the injected field does not have a generic type, like
DataGridinstead ofDataGrid<MyEntity>. Provides a quick-fix. -
Check that Event Handler is implemented correctly:
-
Event Handler must be located only inside the view controller.
-
Event Handler must have a void return type.
-
Event Handler must have a single argument with a type that extends
java.util.EventObject. -
Unable to find specified UI component.
-
-
Check installed delegates. Possible messages:
-
The delegate can be installed only inside the view controller.
-
Unable to find installation point for delegate.
-
Installation point must be a method with a
voidreturn type and a single,FunctionalInterfacetype parameter. -
Unable to find specified UI component.
-
-
Highlight suspicious assignments to fields that are assumed to be injected by the container.
-
Check that GUI components are created by using
ComponentsFactory.createComponent().
-
- Quick-Fixes and Intentions
-
-
Edit view permissions for different resource roles.
-
Create XML descriptor for the view controller.
-
Navigate to the menu item from the controller.
-
-
Logging
- Inspections
-
-
Check that the
org.slf4j.Loggerlogger is used instead ofSystem.out.println(),System.err.println()andjava.lang.ThrowableprintStackTrace(). -
Highlight apache-commons logging statements that lose exception stack trace.
-
-
Menu
- Inspections
-
-
Check that menu doesn’t have duplicated items.
-
-
Security
- Inspections
-
-
Check duplicate code fields in resource roles.
-
Check duplicate name field in resource roles.
-
Check the existence of a view in a project.
-
Check entity attribute policy in resource roles.
-
-
Beans and Services
- Inspections
-
-
Check that the service bean is the correct Jmix framework bean.
-
