Vector Layers
VectorLayer is a base layer for displaying entities on the map. It is a data-aware component acting as a connector between data (geo-objects) and a map. Vector layers enable simple displaying, interactive editing, and drawing geo-objects on a map.
Geo-objects
Geo-object is an entity having a property of a geometry type. This property should have one of the geo-specific datatypes that are included in the io.jmix.maps.datatype package:
Datatype |
Java type |
geoPoint |
org.locationtech.jts.geom.Point |
geoPolyline |
org.locationtech.jts.geom.LineString |
geoPolygon |
org.locationtech.jts.geom.Polygon |
To add the property, create a new attribute and select a geo-specific datatype from the list.
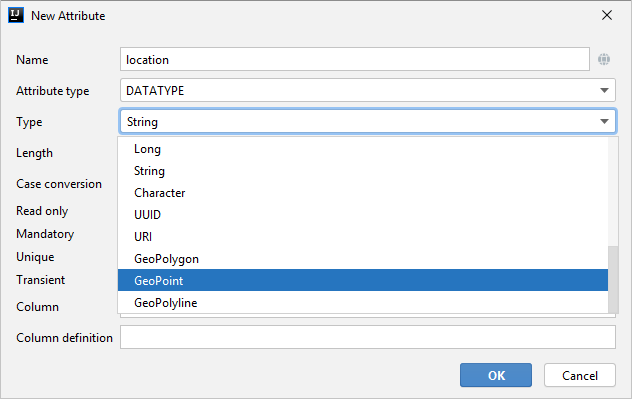
Open code of the entity and add the following annotations:
-
@Geometry— marks that the property is to be used when displaying the geo-object on a map.Geo-object must have one geometry property, otherwise an exception will be thrown when drawing the layer. -
@Convert— allows you to specify a custom JPA converter defining how the datatype will be persisted.By default, the add-on uses JPA converters that transform coordinates into the WKT format which consequently persists as a text. While loading from DB this text will be parsed back into the objects. These converters are included in the package: io.jmix.maps.converter.wkt.
An example of geo-object Order:
@JmixEntity
public class Order {
//...
@Geometry
@PropertyDatatype("geoPoint")
@Column(name = "LOCATION")
@JmixProperty
private Point location;
//...
}As you can see, Order is a simple entity, one of which properties location is of the org.locationtech.jts.geom.Polygon type.
Binding Geo-Objects to a Layer
To bind geo-objects to a layer, you need to pass a datacontainer to the vector layer. This can be declared in the XML descriptor:
<maps:layers selectedLayer="orderLayer">
<maps:tile id="tileLayer" tileProvider="map_OpenStreetMap"/>
<maps:vector id="orderLayer" dataContainer="orderDc" editable="true"/>
</maps:layers>id and dataContainer are required parameters. Vector layer works with both InstanceContainer and CollectionContainer.
editable parameter defines that the layer can be modified.
To edit/draw geometries on the editable vector layer, specify the layer in the selectedLayer parameter of the layers section.
|
Additionally, you can create VectorLayer in the screen controller:
@Autowired
private GeoMap map;
@Autowired
private InstanceContainer<Order> orderDc;
@Subscribe
public void onBeforeShow(BeforeShowEvent event) {
VectorLayer<Order> orderLayer = new VectorLayer<>("orderLayer", orderDc);
orderLayer.setEditable(true);
map.addLayer(orderLayer);
map.selectLayer(orderLayer);
}Setting Geometry Style
To determine geometry style for geo-objects, use setStyleProvider() method. You can also perform this declaratively using the @Install annotation in the screen controller, for example:
@Autowired
private GeometryStyles geometryStyles;
@Install(to = "map.territoryLayer", subject = "styleProvider")
private GeometryStyle mapTerritoryLayerStyleProvider(Territory territory) {
return geometryStyles.polygon()
.setFillColor("#08a343")
.setStrokeColor("#004912")
.setFillOpacity(0.3)
.setStrokeWeight(1);
}Use io.jmix.mapsui.component.layer.style.GeometryStyles bean to create styles for different geometry types.
Working with Selected Geo-Objects
Geo-objects can be selected by user click or automatically from the associated data container. If VectorLayer is set as selected, it becomes interactive, which means a user can select a geo-object by clicking on it.
setSelectedGeoObject() method sets the geo-object which the layer is focused on. For example, if an entity is opened in the editor screen it will be implicitly selected in a corresponding vector layer.
VectorLayer is subscribed to changes in the corresponding data container and automatically refreshes when new items are added to the data container or in case of removing items from the container.
Selecting a geo-object produces the GeoObjectSelectedEvent. You can subscribe to this event in the screen controller, for example, to select the geo-object in the table:
@Autowired
private GroupTable<Order> ordersTable;
@Subscribe("map.orderLayer")
public void onMapOrderLayerGeoObjectSelected(VectorLayer.GeoObjectSelectedEvent<Order> event) {
ordersTable.setSelected(event.getItem());
}Clustering
For a vector layer consisting of geo-points it is possible to group nearby points into clusters:
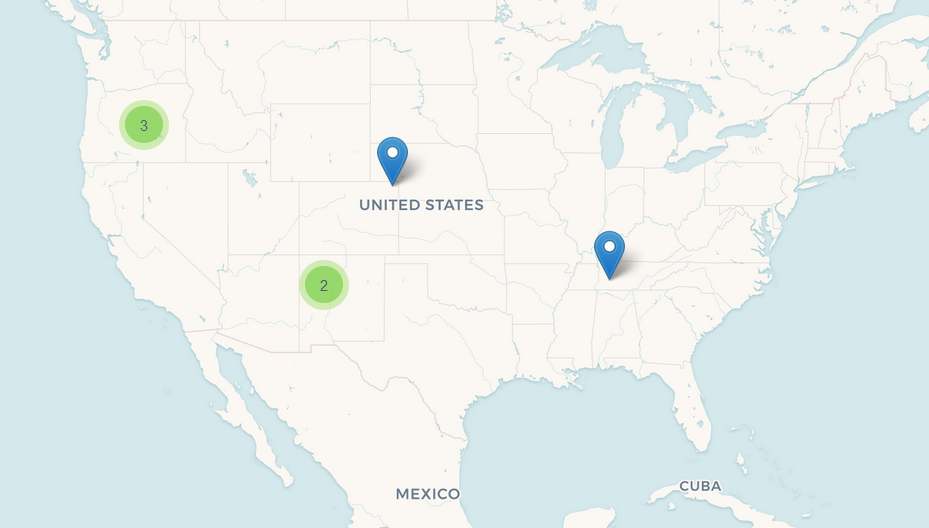
To enable clustering, add the cluster element inside vector in the XML descriptor:
<maps:layers>
<maps:tile id="tiles" tileProvider="sample_CartoTileProvider"/>
<maps:vector id="orders" dataContainer="ordersDc">
<maps:cluster/>
</maps:vector>
</maps:layers>You can specify additional clustering options:
-
radius— maximum radius that a cluster will cover in pixels. The default value is80. -
weightProperty— if specified, then each point of the layer will have a weight value (int) defined by the weight property of the geo-object. This value will be used when calculating the summed up value of the cluster (by default, the number of points is used). -
showCoverage— shows bounds of the cluster when hovering a mouse over it. -
disableAtZoom— specifies a zoom level from which clustering will be disabled. -
showSinglePointAsCluster— shows a single point as a cluster of 1 size.
Working with Underlying Vaadin Components of Geo-objects
For each geo-object displayed on a map, the add-on creates an instance of the io.jmix.mapsui.component.leaflet.translators.GeoObjectWrapper class that keeps the underlying Vaadin Component. This class provides methods to work directly with the wrapped component:
-
openPopup()— opens the pop-up window of the geo-object if the pop-up content is specified. -
closePopup()— closes the pop-up window of the geo-object. -
openTooltip()— opens the tooltip of the geo-object if the tooltip content is specified. -
closeTooltip()— closes the tooltip of the geo-object. -
getLeafletComponent()— returns the underlying Vaadin Component connected with the Leaflet component on the client side.
To obtain geo-object wrappers for a vector layer, invoke the getGeoObjectWrappersMap() method of the GeoMapImpl class (implementation of the GeoMap) and pass the layer to it:
VectorLayer<Order> ordersLayer = map.getLayer("orderLayer");
Map<?, GeoObjectWrapper<Order>> geoObjectWrappersMap =
((GeoMapImpl) map).getGeoObjectWrappersMap(ordersLayer);The returned map contains entries in which keys are geo-objects IDs (or geo-objects themselves for those whose ID = null) and values are corresponding GeoObjectWrapper instances. So you can obtain GeoObjectWrapper of the particular geo-object this way:
@Autowired
private GroupTable<Order> ordersTable;
@Subscribe("map.orderLayer")
public void onMapOrderLayerGeoObjectSelected(VectorLayer.GeoObjectSelectedEvent<Order> event) {
ordersTable.setSelected(event.getItem());
GeoObjectWrapper<Order> geoObjectWrapper = geoObjectWrappersMap.get(event.getItem().getId());
if (geoObjectWrapper != null) {
geoObjectWrapper.openPopup();
}
}
If the geometry value of the geo-object is null, then there is no GeoObjectWrapper for this geo-object.
|
Also, be aware that GeoObjectWrapper instances can be changed or replaced after refreshing the layer. So always use this map to get the relevant wrapper instance.
