Geo-objects
A geo-object, short for geospatial object, refers to an entity having a property of a geometry type. The add-on supports the following geo-specific types that comes from the JTS Topology Suite (JTS) library:
Datatype |
Java type |
GeoPoint |
org.locationtech.jts.geom.Point |
GeoPolyline |
org.locationtech.jts.geom.LineString |
GeoPolygon |
org.locationtech.jts.geom.Polygon |
To add the property, create a new attribute and select a geo-specific datatype from the list.
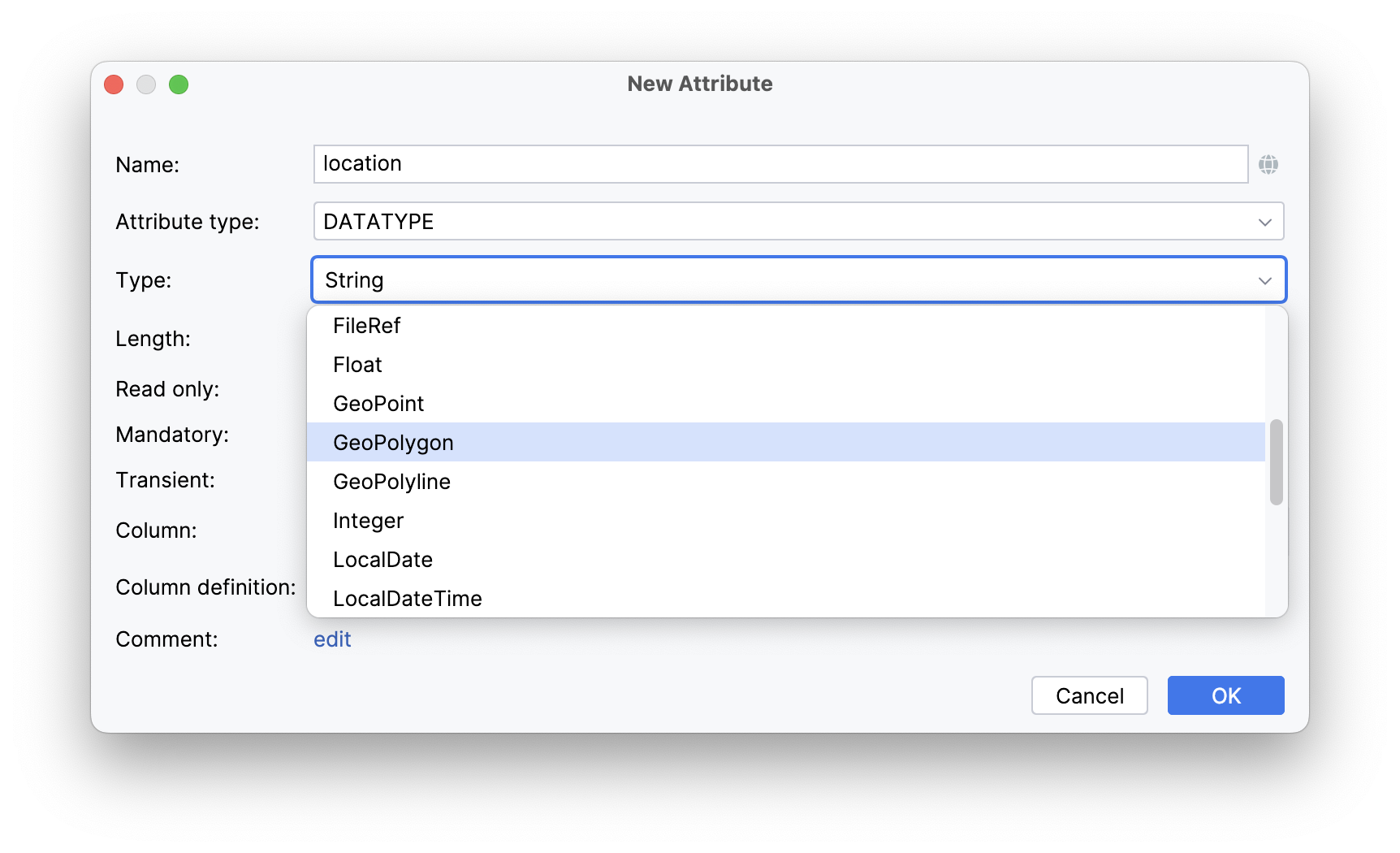
An example of geo-object Location:
@JmixEntity
@Table(name = "LOCATION")
@Entity
public class Location {
@Column(name = "BUILDING", nullable = false)
@NotNull
private Point building;
}As you can see, Location is a simple entity, one of which properties building is of the org.locationtech.jts.geom.Point type.
To bind geo-objects to a vector layer, you need to use DataVectorSource.
Coordinates
The Coordinate class in JTS encapsulates a pair of X and Y coordinates that define a point in 2D space.
Geometry objects - Point, LineString, Polygon - are created using the given Coordinate.
Let’s take a closer look at the examples below.
-
POINT (13.347796079315284 52.55344847222085)The first X-ordinate is longitude. The second Y-ordinate is latitude.
-
LINESTRING (13.346886063248354 52.553529790121985, 13.347394863347068 52.5532539371346, 13.347837668453902 52.55355180648286, 13.347860653822895 52.553536712270784)A
LineStringis defined by a sequence of coordinates that delineate the vertices along the line. These coordinates are stored in a specific order to represent the continuous path of the line. The first X-ordinate in each point pair represents the longitude, while the second one represents the latitude.
